

Each time the armature rotates by 180°, the position of the north and south poles is reversed. In that design, DC running through the wire winding creates the magnetic field. They are known as the original DC motors because their design is dating back to Sprague’s initial design, who invented the first practical DC motor design in 1886 (1). And, there are two different designs for DC motors, depending on the commutator standard, under which all DC motors types are classified - brushed DC motors and brushless DC motor.īrushed DC motors, which are also known as the original DC motors, generate torque directly from DC power supplied to the motor, using internal commutation, stationary magnets (permanent or electromagnets), and rotating electromagnets. In today’s field of engineering and technology, you can find different types of direct current (DC) motors specialized for varying tasks and features for diverse electronics projects. This interplay of magnetic fields and moving charged particles (the electrons in the current) generates the torque that makes the armature spin.

The armature experiences a force described by the left-hand rule. The key to producing motion is positioning the electromagnet within the magnetic field of the permanent magnet (its field runs from its north to south poles). The armature, carrying current provided by the battery, is an electromagnet because a current-carrying wire generates a magnetic field invisible magnetic field lines are circulating all around the wire of the armature.

The motor features a permanent horseshoe magnet (called the stator because it’s fixed in place) and a turning coil of wire called an armature (or rotor, because it rotates). But, how are they able to convert the electrical energy to the mechanical rotation? In other words, DC motors take electrical power through direct current and transform this energy into mechanical rotation. What is a DC Motor?Ī direct current (DC) motor is a type of electric machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy with the help of the magnetic field generated in the device. Even though you are a novice in programming with Arduino or creating electronics projects with DC motors, it is simple to use them with a few lines of code, and some necessary components, depending on which method you use, will be explained later. The PWM signals has a resolution of 8 bits which means the duty cycle can vary between 0 and 255.In this article, I will give you information about DC motors, also known as electronic motors, and how you can control them using Arduino to create electronics projects with mobility and agility easily. The resolution of the Arduino UNO ADC is 10 bits which means the digital output value is between. Using the X-axis and the Y-axis potentiometers we can control two DC motors independently.
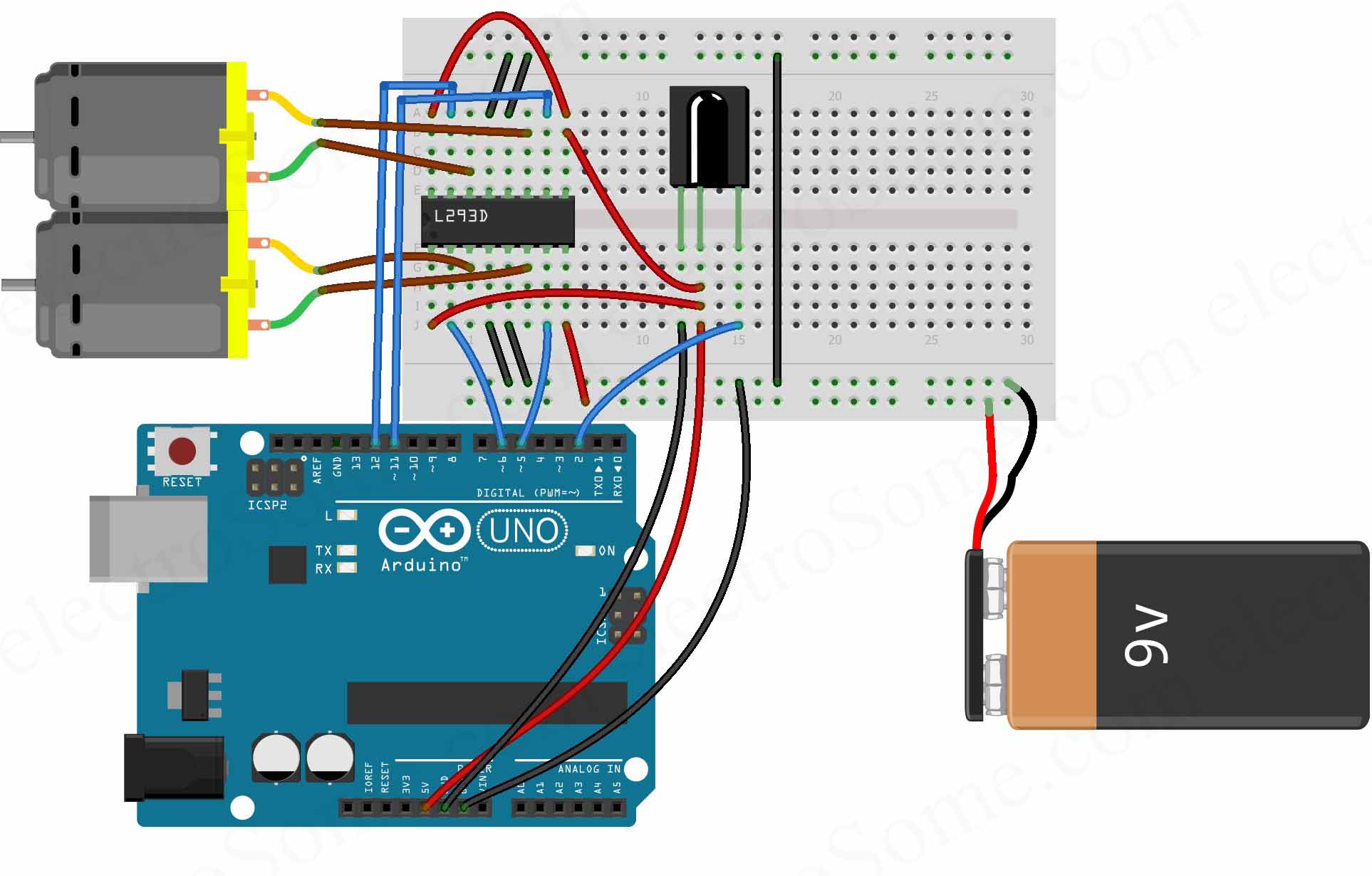
The switch pin (SW) is not used in this example. The output of the X-axis potentiometer is connected to Arduino analog pin A0, Y-axis potentiometer output can be used to control the DC motor. SW is the push button terminal (the other terminal is connected to GND). The joystick board has 5 terminals: GND, +5V, VRX, VRY and SW where: The active PWM pin decides the motor direction of rotation (one at a time, the other output is logic 0). Pins 9 and 10 are PWM signal outputs, at any time there is only 1 active PWM, this allows us to control the direction of rotation as well as the speed by varying the duty cycle of the active PWM signal. As shown in the circuit diagram we need only 3 Arduino terminal pins: A0 (analog pin), pin 9 and pin 10.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
